

The stimulus may disappear, but the memory will remain and we can remember how good or bad it felt.Īdditionally, sensory memory has a fundamental impact when it comes to learning, because this process usually involves other cognitive processes. In fact, it makes the experience more complete by allowing us to perceive different stimuli. Then, the importance of sensory memory and the different kinds of it are what add sense to the experience. This is what determines whether we store the information temporarily or on a longer basis. Lastly, we give significance to the stimulus. Later, it follows a pattern recognition process, through which we associate new information with an existing pattern. Perception works by paying attention to the stimuli received. By that, we mean we store it temporarily. When it comes to the sensory kind, it’s in charge of retaining stimulus in the sensory registries before we lose the information. You may like: What to Eat to Improve Memory and Tips to Stimulate Your Brain The functions and benefits of stimulating this kind of memoryĪccording to the modal model Bruning details, memory is a group of retention systems. Of course, how long this auditory stimulus remains in our mind also depends on its intensity and the impact that it has on us. This is the type that’s in charge of mediating between the auditory stimulus and the memory.Īlthough it’s the type of sensory memory that lasts for the shortest amount of time, when it comes to visual memory (which can retain five to seven fragments of information up to four seconds), we can also create auditory sensory images that we can store for longer.
It allows us to examine objects through touching and interacting with them. This type of memory manages to work with around four or five items simultaneously, with which we can interact at the same time as touching, moving, lifting, and sliding, among others. By that, we mean that we use both proprioception and interception in tactile sensory memory. As its name suggests, it’s the kind that touch activates through those stimuli that reach the skin.Īlthough it’s also what we experience through the muscles, joints, and tendons. You may also be interested in: Memory Loss and Forgetfulness: Are They Normal? 2. Here, we’re employing nothing more than our iconic memory! They start face down, and then you turn them over and try to guess where the other one is to form a pair. In fact, there’s the one where you have cards with patterns or pictures on them in sets of two. For those details to stay locked in our memory for the long term, it depends on how much significance we give them.Īs an example, although it may seem obvious, think of the many different types of memory training games. It’s very useful because later we have processes that allow us to analyze and interpret what happened. Through this type, we’re able to remember many objects and details of a scene or situation in a few seconds. Let’s take a look at each one of them to explain them better. We have three types of sensory memory: iconic, haptic, and echoic. Sensory memory ties processes of perception with that of cognition. This will be what causes us to specifically remember in the tips of our fingers the pain from that time hot water fell on us.
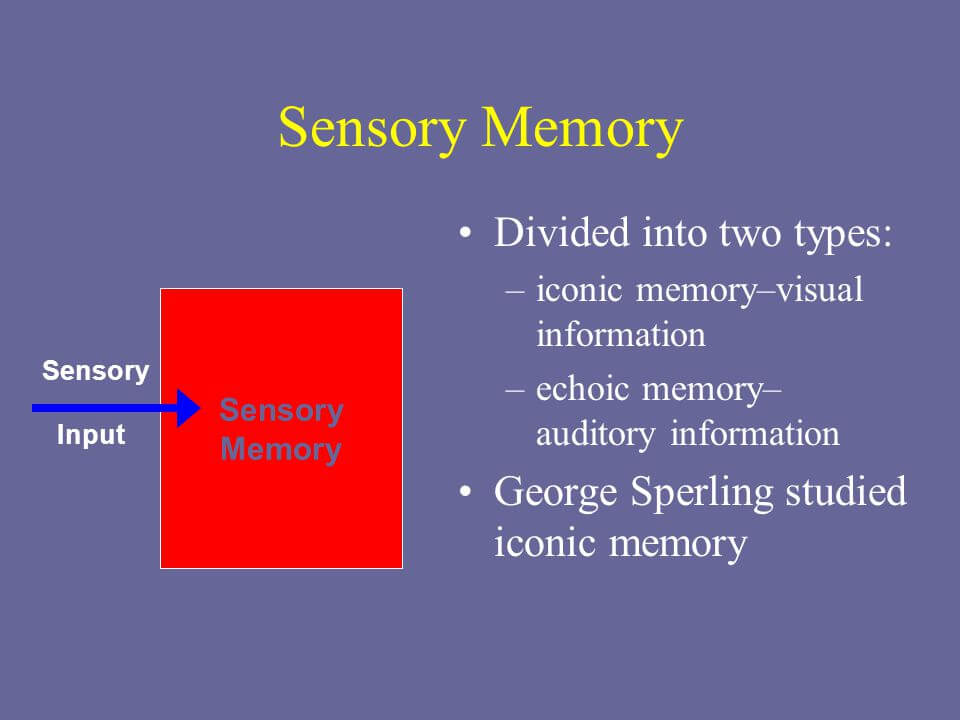
This is why we have three types of sensory memory. However, it doesn’t always work in the same way or part with the same information. It also is fundamental for the development of our intelligence. For that reason, it’s essential for our memories and learning process. Memory uses a group of cerebral processes that are dedicated to interpreting, storing, and recovering information.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
